Token Metadata Program
The Token Metadata Program is used to attach additional data to all tokens on Solana. This allows wallets, dapps and even block explorers to present tokens in a standardized way, creating a uniform user experience across the ecosystem.
To enhance Mint Accounts with additional metadata, the Metadata program uses a concept called Program Derived Addresses (PDA).
Program Derived Addresses (PDAs)
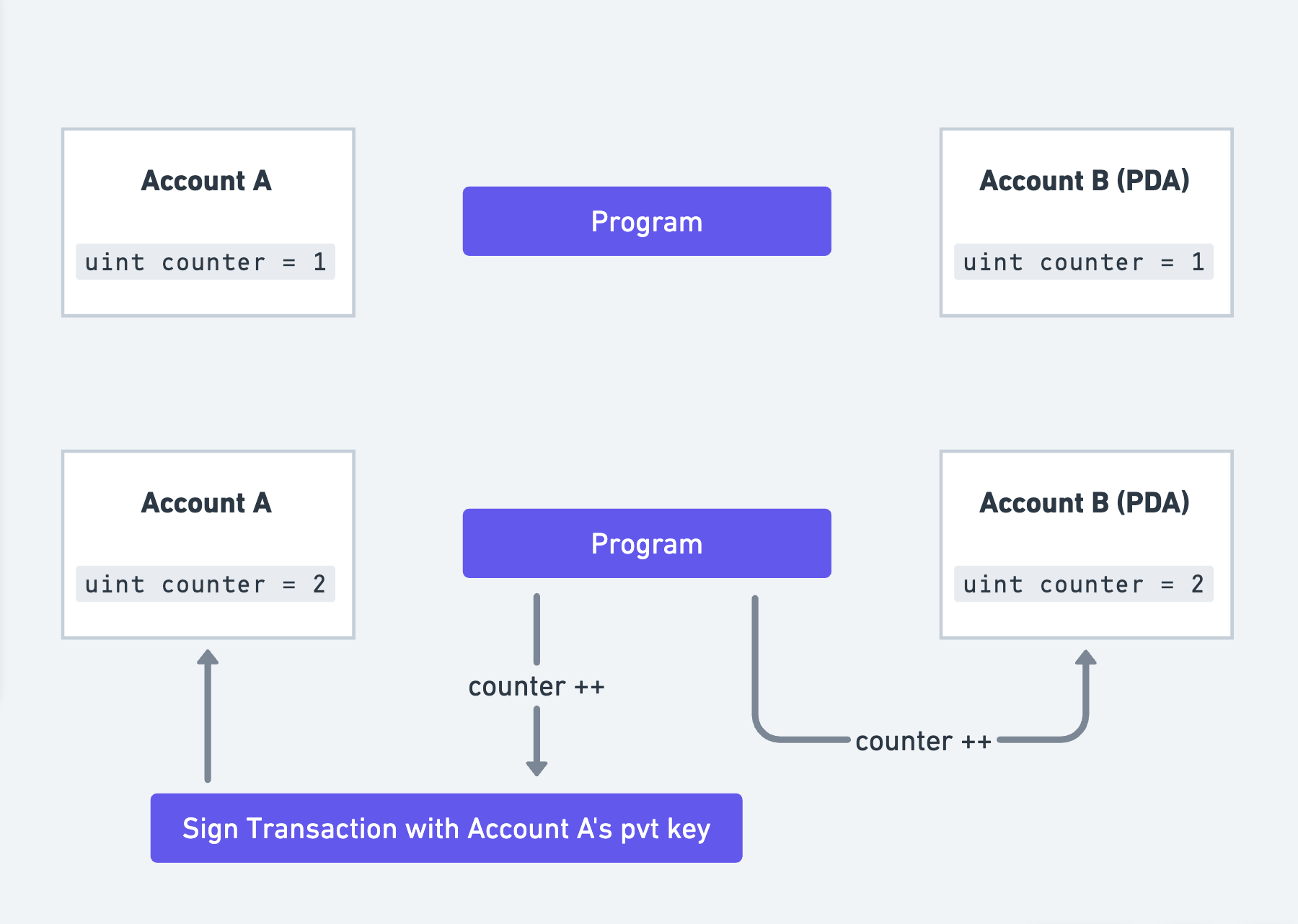
When we discussed Accounts, we talked about the need for the account's owner to sign transactions whenever a program makes a change to the said account.
This is problematic and not always possible. Imagine a use-case where we are counting the number of tokens in a given account and this number needs to be saved on-chain. The account's owner will have to sign transactions each time this number changes.
An ingenious solution to this is PDAs. PDAs envelop accounts that can be programmatically controlled by certain programs. This allows programs to sign on behalf of these accounts without requiring a private key, as shown below.
PDAs are deterministically derived from a
program_idand a string (also known as seeds) like"auction_house"or"token_metadata". If you want to dive deep into how PDAs are generated, I highly recommend reading Solana Cookbook's PDA guide.
To attach additional data to a Mint Account, the Token Metadata Program derives a PDA from the Mint Account’s address. This PDA is then used to store a Metadata Account with the Mint Account using a PDA as shown below.
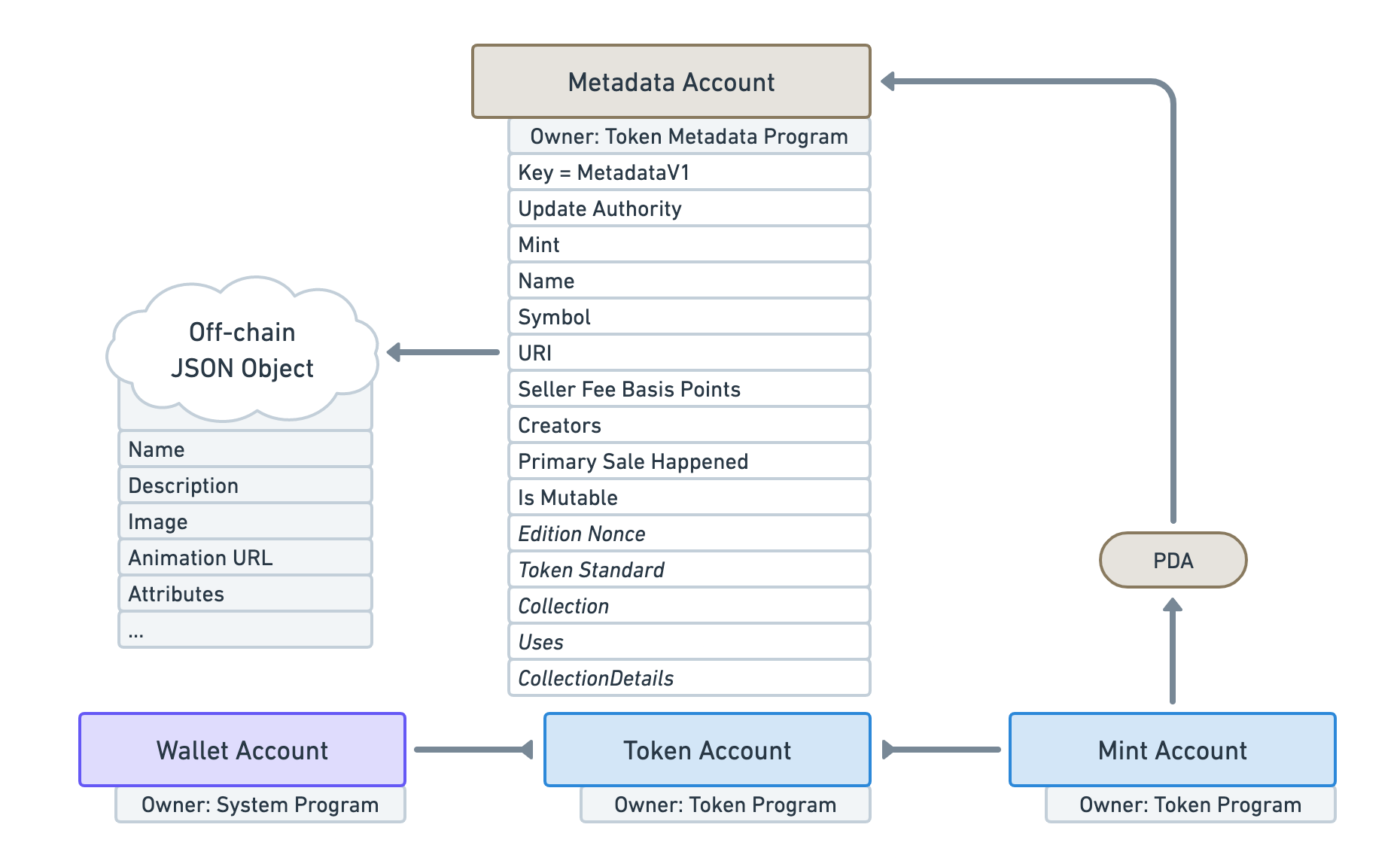
A Metadata account stores lots of useful information that Mint Accounts could not provide. This account also has a URI field which points to an off-chain JSON object. This object saves information like the image and attributes for an NFT.
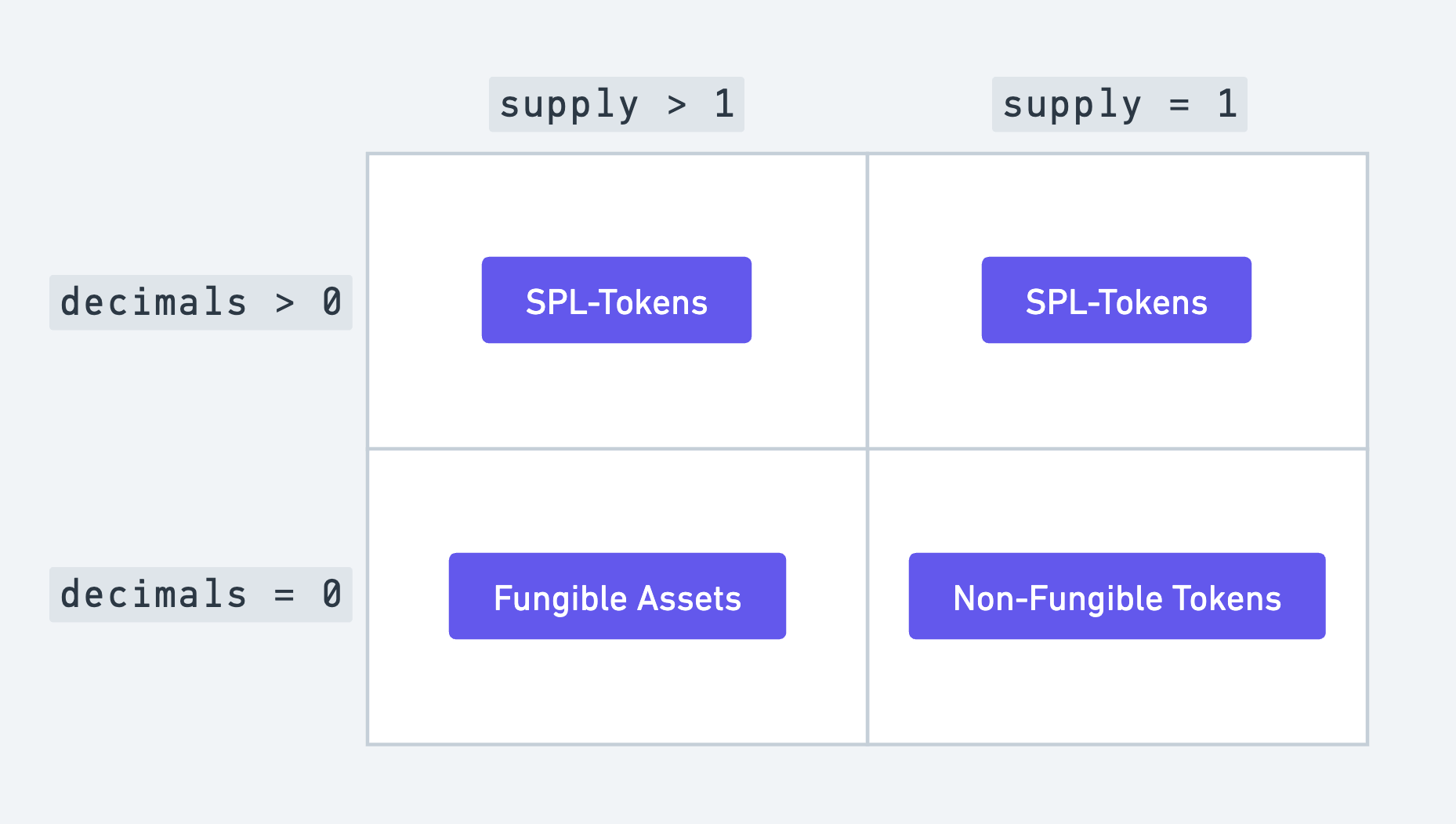
The combination of the Token Program and the Token Metadata Program allows tokens to be categorised into three broad categories depending on two characteristics:
-
supply: the total number of tokens in circulation. -
decimal places: the number of decimals points a token is allowed to have. For example: SOL is allowed to have 9 decimal points, which means, 10^-9 SOL is a valid denomination and can be transferred between wallets.